Xray Affect the Baby on 3wee of Pregnancy
-
Genetic Screening
-
First Trimester
-
Second Trimester
-
Ultrasound
-
Amniocentesis
-
Chorionic Villus Sampling
-
Fetal Monitoring
-
Glucose
-
Group B Strep Civilization
Your health care provider may recommend a multifariousness of screenings, tests and imaging techniques during your pregnancy. These tests are designed to provide information nigh the wellness of your babe and may help you lot optimize your child'due south prenatal intendance and evolution.
Genetic Screening
Many genetic abnormalities tin be diagnosed before birth. Your doctor or midwife may recommend genetic testing during pregnancy if you or your partner has a family unit history of genetic disorders. You may also choose to have genetic screening if you have had a fetus or babe with a genetic aberration.
Examples of genetic disorders that can be diagnosed before nativity include:
-
Cystic fibrosis
-
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
-
Hemophilia A
-
Polycystic kidney disease
-
Sickle cell disease
-
Tay-Sachs disease
-
Thalassemia
The following screening methods are available during pregnancy:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test or multiple marking test
-
Amniocentesis
-
Chorionic villus sampling
-
Prison cell-free fetal DNA testing
-
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (withdrawing a small sample of the fetal blood from the umbilical cord)
-
Ultrasound browse
First Trimester Prenatal Screening Tests
Kickoff trimester screening is a combination of fetal ultrasound and maternal claret testing. This screening procedure can help make up one's mind the risk of the fetus having certain birth defects. Screening tests may be used alone or with other tests.
Starting time trimester screening includes:
-
Ultrasound for fetal nuchal translucency. Nuchal translucency screening uses an ultrasound to examine the surface area at the back of the fetal cervix for increased fluid or thickening.
-
Ultrasound for fetal nasal bone determination. The nasal os may not be visualized in some babies with certain chromosome abnormalities, such as Down syndrome. This screen is performed using an ultrasound between 11 and 13 weeks gestation.
-
Maternal serum (blood) tests. These blood tests measure two substances constitute in the blood of all pregnant women:
-
Pregnancy-associated plasma poly peptide A. A protein produced past the placenta in early on pregnancy. Abnormal levels are associated with an increased chance of chromosomal abnormality.
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin. A hormone produced past the placenta in early pregnancy. Abnormal levels are associated with an increased hazard of chromosomal abnormality.
-
When used together equally first trimester screening tests, nuchal translucency screening and maternal blood tests accept a greater ability to decide if the fetus might have a birth defect, such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21) and trisomy 18.
If the results of these first trimester screening tests are abnormal, genetic counseling is recommended. Additional testing, such as chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, cell-complimentary fetal DNA or other ultrasounds, may be needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Second Trimester Prenatal Screening Tests
Second trimester prenatal screening may include several claret tests called multiple markers. These markers provide information about your potential take a chance of having a baby with certain genetic conditions or birth defects. Screening is usually done by taking a sample of your blood between xv and 20 weeks of pregnancy (16 to 18 weeks is platonic). The multiple markers include:
-
AFP screening. Also called maternal serum AFP, this blood test measures the level of AFP in your blood during pregnancy. AFP is a protein normally produced past the fetal liver that is present in the fluid surrounding the fetus (amniotic fluid). It crosses the placenta and enters your blood. Abnormal levels of AFP may indicate:
-
A miscalculated due date, equally the levels vary throughout pregnancy
-
Defects in the abdominal wall of the fetus
-
Down syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities
-
Open neural tube defects, such as spina bifida
-
Twins (more than 1 fetus is producing the protein)
-
-
Estriol. This is a hormone produced by the placenta. It tin can be measured in maternal blood or urine to exist used to determine fetal health.
-
Inhibin. This is a hormone produced by the placenta.
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin. This is also a hormone produced by the placenta.
Abnormal test results of AFP and other markers may hateful that additional testing is needed. An ultrasound is used to confirm the milestones of your pregnancy and to check the fetal spine and other trunk parts for defects. An amniocentesis may be needed for an authentic diagnosis.
Since multiple marker screening is not diagnostic, it is non 100 per centum accurate. It helps determine who in the population should be offered additional testing during pregnancy. False-positive results may bespeak a problem when the fetus is actually healthy. On the other hand, false-negative results signal a normal result when the fetus actually does have a health problem.
When you take both first and 2nd trimester screening tests performed, the ability of the tests to notice an abnormality is greater than using but 1 screening independently. Well-nigh cases of Down syndrome can be detected when both first and second trimester screenings are used.
Ultrasound

An ultrasound browse is a diagnostic technique that uses loftier-frequency sound waves to create an image of the internal organs. A screening ultrasound is sometimes done during the course of your pregnancy to check normal fetal growth and verify the due date.
When are ultrasounds performed during pregnancy?
Ultrasounds may be done at various times throughout pregnancy for several reasons:
First Trimester
-
To establish the due engagement (this is the about authentic way of determining the due engagement)
-
To make up one's mind the number of fetuses and identify placental structures
-
To diagnose an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage
-
To examine the uterus and other pelvic anatomy
-
To detect fetal abnormalities (in some cases)
Midtrimester (likewise called the 18- to 20-week scan)
-
To confirm the due date (a due date set up in the start trimester is rarely inverse)
-
To determine the number of fetuses and examine the placental structures
-
To assistance in prenatal tests, such as an amniocentesis
-
To examine the fetal anatomy for abnormalities
-
To check the corporeality of amniotic fluid
-
To examine blood flow patterns
-
To observe fetal behavior and activity
-
To measure the length of the neck
-
To monitor fetal growth
Third Trimester
-
To monitor fetal growth
-
To check the amount of amniotic fluid
-
To conduct the biophysical profile test
-
To determine the position of the fetus
-
To assess the placenta
How is an ultrasound scan performed?
Two types of ultrasounds can be performed during pregnancy:
-
Abdominal ultrasound. In an abdominal ultrasound, gel is applied to your abdomen. The ultrasound transducer glides over the gel on the belly to create the image.
-
Transvaginal ultrasound. In a transvaginal ultrasound, a smaller ultrasound transducer is inserted into your vagina and rests against the dorsum of the vagina to create an epitome. A transvaginal ultrasound produces a sharper image than an intestinal ultrasound and is often used in early pregnancy.
Which ultrasound imaging techniques are available?
There are several types of ultrasound imaging techniques. Every bit the most common type, the 2-D ultrasound provides a apartment picture show of 1 attribute of the babe.
If more than information is needed, a iii-D ultrasound exam tin can be done. This technique, which provides a 3-D motion picture, requires a special car and special training. The three-D image allows the health care provider to see the width, meridian and depth of the images, which can exist helpful during the diagnosis. The 3-D images tin as well be captured and saved for later review.
The latest technology is 4-D ultrasound, which allows the health intendance provider to visualize the unborn baby moving in real time. With 4-D imaging, a three-dimensional epitome is continuously updated, providing a "live activity" view. These images frequently have a aureate color, which helps show shadows and highlights.
Ultrasound images may be captured in withal photographs or on video to document findings.
What are the risks and benefits of ultrasound imaging?
Fetal ultrasound has no known risks other than mild discomfort due to pressure from the transducer on your abdomen or in your vagina. No radiation is used during the procedure.
Transvaginal ultrasound requires covering the ultrasound transducer in a plastic or latex sheath, which may crusade a reaction in women with a latex allergy.
Ultrasound imaging is constantly existence improved and refined. As with whatever test, the results may not be completely accurate. Nonetheless, an ultrasound can provide valuable information to parents and health care providers, helping them manage and care for the pregnancy and the baby. In improver, ultrasound imaging gives parents a unique opportunity to come across their babe before birth, helping them to bond and plant an early relationship.
Fetal ultrasound is sometimes offered in nonmedical settings to provide emblem images or videos for parents. While the ultrasound process itself is considered condom, it is possible that untrained personnel may miss an abnormality or give parents false assurances about their infant'south well-beingness. It is best to have an ultrasound performed past trained medical personnel who tin correctly translate the results. Talk with your doc or midwife if yous accept questions.
Amniocentesis
An amniocentesis involves taking a pocket-sized sample of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus. It is used to diagnose chromosomal disorders and open up neural tube defects, such equally spina bifida. Testing is available for other genetic defects and disorders depending on your family history and the availability of lab testing at the time of the procedure.
Who is an ideal candidate for amniocentesis?
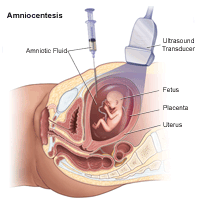
An amniocentesis is generally offered to women between the 15th and 20th calendar week of pregnancy who have an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities. Candidates include women who will be over age 35 at the time of delivery or those who accept had an abnormal maternal serum screening test.
How is an amniocentesis performed?
An amniocentesis involves inserting a long, sparse needle through your abdomen into the amniotic sac to withdraw a small sample of amniotic fluid. The amniotic fluid contains cells shed by the fetus, which incorporate genetic information. Although specific details of each procedure may vary, a typical amniocentesis follows this procedure:
-
Your belly will be cleansed with an antiseptic.
-
Your doctor may or may not give a local anesthetic to numb the pare.
-
Your md volition employ ultrasound technology to help guide a hollow needle into the amniotic sac. He or she volition withdraw a minor sample of fluid for lab assay.
You may feel some cramping during or after the amniocentesis. Strenuous activities should be avoided for 24 hours post-obit the procedure.
Women who are pregnant with twins or other higher-order multiples need sampling from each amniotic sac to study each infant. Depending on the position of the baby and placenta, corporeality of fluid, and woman's anatomy, sometimes the amniocentesis cannot be washed. The fluid is then sent to a genetics lab so that the cells can grow and exist analyzed. AFP is as well measured to dominion out an open neural tube defect. Results are usually available in almost 10 days to two weeks, depending on the lab.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)?
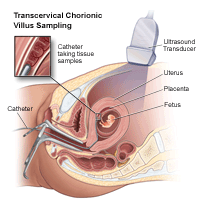
CVS is a prenatal test that involves taking a sample of some of the placental tissue. This tissue contains the same genetic material as the fetus and can be tested for chromosomal abnormalities and some other genetic problems. Testing is available for other genetic defects and disorders, depending on your family history and the availability of lab testing at the time of the procedure. Unlike amniocentesis, CVS does not provide information on open neural tube defects. Therefore, women who undergo CVS besides demand a follow-up blood test between 16 and eighteen weeks of pregnancy to screen for these defects.
How is CVS performed?
CVS may be offered to women with an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities or who have a family unit history of a genetic defect that is testable from the placental tissue. CVS is usually performed betwixt the 10th and 13th week of pregnancy. Although exact methods may vary, the process involves the following steps:
-
Your doc will insert a small tube (catheter) through your vagina and into your cervix.
-
Using ultrasound engineering, your dr. will guide the catheter into place almost the placenta.
-
Your doctor will remove some tissue using a syringe on the other end of the catheter.
Your doctor may as well choose to perform a transabdominal CVS, which involves inserting a needle through your abdomen and into your uterus to sample the placental cells. You may feel some cramping during and after either type of CVS process. The tissue samples are sent to a genetic lab for growth and analysis. Results are usually available in about 10 days to two weeks, depending on the lab.
What if CVS is not possible?
Women with twins or other higher-order multiples commonly demand sampling from each placenta. However, because of the complexity of the procedure and the positioning of the placentas, CVS is non e'er feasible or successful with multiples.
Women who are not candidates for CVS or who did non get accurate results from the procedure may crave a follow-up amniocentesis. An active vaginal infection, such as herpes or gonorrhea, volition prohibit the procedure. In other cases, the medico may take a sample that does not have enough tissue to grow in the lab, generating incomplete or inconclusive results.
Fetal Monitoring
During late pregnancy and labor, your md may desire to monitor the fetal heart rate and other functions. Fetal centre rate monitoring is a method of checking the rate and rhythm of the fetal heartbeat. The average fetal heart charge per unit is between 120 and 160 beats per minute. This charge per unit may modify as the fetus responds to weather in the uterus. An aberrant fetal heart rate or design may mean that the fetus is not getting plenty oxygen or indicate other problems. An aberrant pattern also may mean that an emergency cesarean commitment is needed.
How is fetal monitoring performed?
Using a fetoscope (a type of stethoscope) to listen to the fetal heartbeat is the virtually basic type of fetal eye charge per unit monitoring. Some other type of monitoring is performed with a hand-held Doppler device. This is often used during prenatal visits to count the fetal heart rate. During labor, continuous electronic fetal monitoring is often used. Although the specific details of each process may vary, standard electronic fetal monitoring follows this process:
-
Gel is applied to your abdomen to deed as a medium for the ultrasound transducer.
-
The ultrasound transducer is fastened to your belly with straps and then it tin can transmit the fetal heartbeat to a recorder. The fetal heart charge per unit is displayed on a screen and printed onto special newspaper.
-
During contractions, an external tocodynamometer (a monitoring device that is placed over the peak of the uterus with a belt) can record the pattern of contractions.
When is internal fetal monitoring needed?
On occasion, internal fetal monitoring is needed to provide a more accurate reading of the fetal eye charge per unit. Your handbag of waters (amniotic fluid) must be broken and your cervix must be partially dilated to employ internal monitoring. Internal fetal monitoring involves inserting an electrode through the dilated neck and attaching the electrode to the scalp of the fetus.
Glucose Testing
Glucose testing is used to measure out the level of sugar in your blood.
A glucose challenge test is unremarkably conducted between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Abnormal glucose levels may signal gestational diabetes.
What is involved in a glucose claiming test?
The initial one-hour test is a glucose challenge test. If the results are abnormal, a glucose tolerance exam is needed.
How is a glucose tolerance examination performed?
You may exist asked to only drink water on the solar day the glucose tolerance test is given. Although the specific details of each procedure may vary, a typical glucose tolerance test includes the following steps:
-
An initial fasting sample of blood will be drawn from your vein.
-
You lot will exist given a special glucose solution to drinkable.
-
Blood will be fatigued at various times over the class of several hours to measure the glucose levels in your body.
Grouping B Strep Culture
Group B streptococcus (GBS) is a type of leaner institute in the lower genital tract of nearly 20 percentage of all women. While a GBS infection does not usually cause problems in women earlier pregnancy, it can cause serious illness in mothers during pregnancy. GBS may crusade chorioamnionitis (a severe infection of the placental tissues) and postpartum infection. Urinary tract infections caused by GBS tin pb to preterm labor and nascence or pyelonephritis and sepsis.
GBS is the most common cause of life-threatening infections in newborns, including pneumonia and meningitis. Newborn babies contract the infection during pregnancy or from the mother'due south genital tract during labor and delivery.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends screening all meaning women for vaginal and rectal GBS colonization between 35 and 37 weeks gestation. The treatment of mothers with sure risk factors or positive cultures is important to reduce the gamble of transmission of GBS to the babe. Babies whose mothers receive antibody handling for a positive GBS test are 20 times less likely to develop the affliction than those without treatment.
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/common-tests-during-pregnancy
Post a Comment for "Xray Affect the Baby on 3wee of Pregnancy"